To intercept HTTP requests, use the
webRequest
API。
This API enables you to add listeners for various stages of making an HTTP request.
In the listeners, you can:
In this article we'll look at three different uses for the
webRequest
模块:
Create a new directory called "requests". In that directory, create a file called "manifest.json" which has the following contents:
{
"description": "Demonstrating webRequests",
"manifest_version": 2,
"name": "webRequest-demo",
"version": "1.0",
"permissions": [
"webRequest",
"<all_urls>"
],
"background": {
"scripts": ["background.js"]
}
}
Next, create a file called "background.js" with the following contents:
function logURL(requestDetails) {
console.log("Loading: " + requestDetails.url);
}
browser.webRequest.onBeforeRequest.addListener(
logURL,
{urls: ["<all_urls>"]}
);
Here we use
onBeforeRequest
to call the
logURL()
function just before starting the request. The
logURL()
function grabs the URL of the request from the event object and logs it to the browser console.
{urls: ["<all_urls>"]}
pattern
means we will intercept HTTP requests to all URLs.
To test it out:
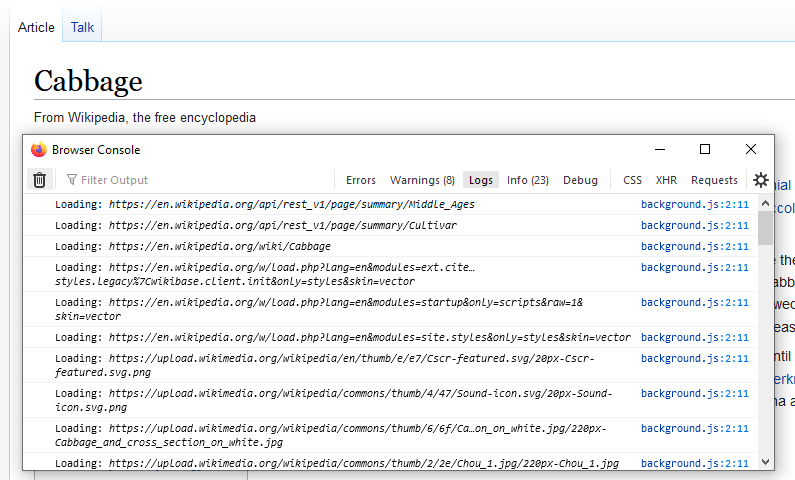
In the Browser Console, you should see the URLs for any resources that the browser requests. For example, this screenshot shows the URLs from loading a Wikipedia page:
Now let's use
webRequest
to redirect HTTP requests. First, replace manifest.json with this:
{
"description": "Demonstrating webRequests",
"manifest_version": 2,
"name": "webRequest-demo",
"version": "1.0",
"permissions": [
"webRequest",
"webRequestBlocking",
"https://developer.mozilla.org/"
],
"background": {
"scripts": ["background.js"]
}
}
The changes here are to:
webRequestBlocking
permission
.
This extra permission is needed when an extension wants to modify a request.
<all_urls>
permission with individual
host permissions
, as this is good practice to minimize the number of requested permissions.
Next, replace background.js with this:
var pattern = "https://developer.mozilla.org/*";
var targetUrl = "https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Add-ons/WebExtensions/Your_second_WebExtension/frog.jpg";
function redirect(requestDetails) {
console.log("Redirecting: " + requestDetails.url);
if (requestDetails.url === targetUrl) {
return;
}
return {
redirectUrl: targetUrl
};
}
browser.webRequest.onBeforeRequest.addListener(
redirect,
{urls:[pattern], types:["image"]},
["blocking"]
);
Again, we use the
onBeforeRequest
event listener to run a function just before each request is made.
This function replaces the
redirectUrl
with the target URL specified in the function. In this case, the frog image from the
your second extension tutorial
.
This time we are not intercepting every request: the
{urls:[pattern], types:["image"]}
option specifies that we should only intercept requests (1) to URLs residing under "https://developer.mozilla.org/" (2) for image resources.
见
webRequest.RequestFilter
for more on this.
Also note that we're passing an option called
"blocking"
: we need to pass this whenever we want to modify the request.
It makes the listener function block the network request, so the browser waits for the listener to return before continuing.
见
webRequest.onBeforeRequest
documentation for more on
"blocking"
.
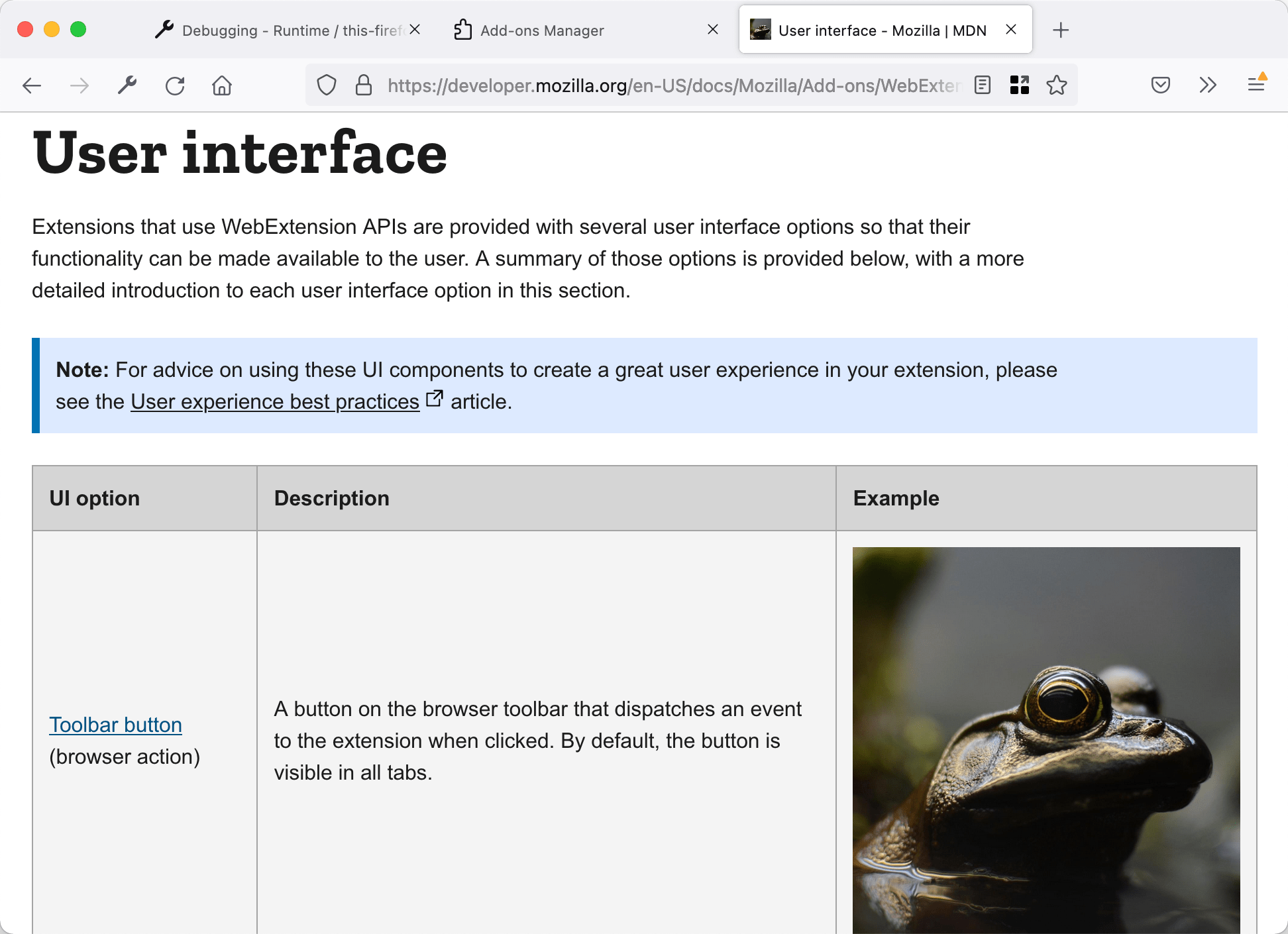
To test it out, open a page on MDN that contains a lot of images (for example the page listing extension user interface components ), reload the extension , and then reload the MDN page. You will see something like this:
Finally we'll use
webRequest
to modify request headers.
In this example we'll modify the "User-Agent" header so the browser identifies itself as Opera 12.16, but only when visiting pages under http://useragentstring.com/".
Update your
manifest.json
to include
http://useragentstring.com/
{
"description": "Demonstrating webRequests",
"manifest_version": 2,
"name": "webRequest-demo",
"version": "1.0",
"permissions": [
"webRequest",
"webRequestBlocking",
"http://useragentstring.com/"
],
"background": {
"scripts": ["background.js"]
}
}
Replace "background.js" with code like this:
var targetPage = "http://useragentstring.com/*";
var ua = "Opera/9.80 (X11; Linux i686; Ubuntu/14.10) Presto/2.12.388 Version/12.16";
function rewriteUserAgentHeader(e) {
e.requestHeaders.forEach(function(header){
if (header.name.toLowerCase() == "user-agent") {
header.value = ua;
}
});
return {requestHeaders: e.requestHeaders};
}
browser.webRequest.onBeforeSendHeaders.addListener(
rewriteUserAgentHeader,
{urls: [targetPage]},
["blocking", "requestHeaders"]
);
Here we use the
onBeforeSendHeaders
event listener to run a function just before the request headers are sent.
The listener function will be called only for requests to URLs matching the
targetPage
pattern
.
Also note that we've again passed
"blocking"
as an option. We've also passed
"requestHeaders"
, which means that the listener will be passed an array containing the request headers that we expect to send.
见
webRequest.onBeforeSendHeaders
for more information on these options.
The listener function looks for the "User-Agent" header in the array of request headers, replaces its value with the value of the
ua
variable, and returns the modified array.
This modified array will now be sent to the server.
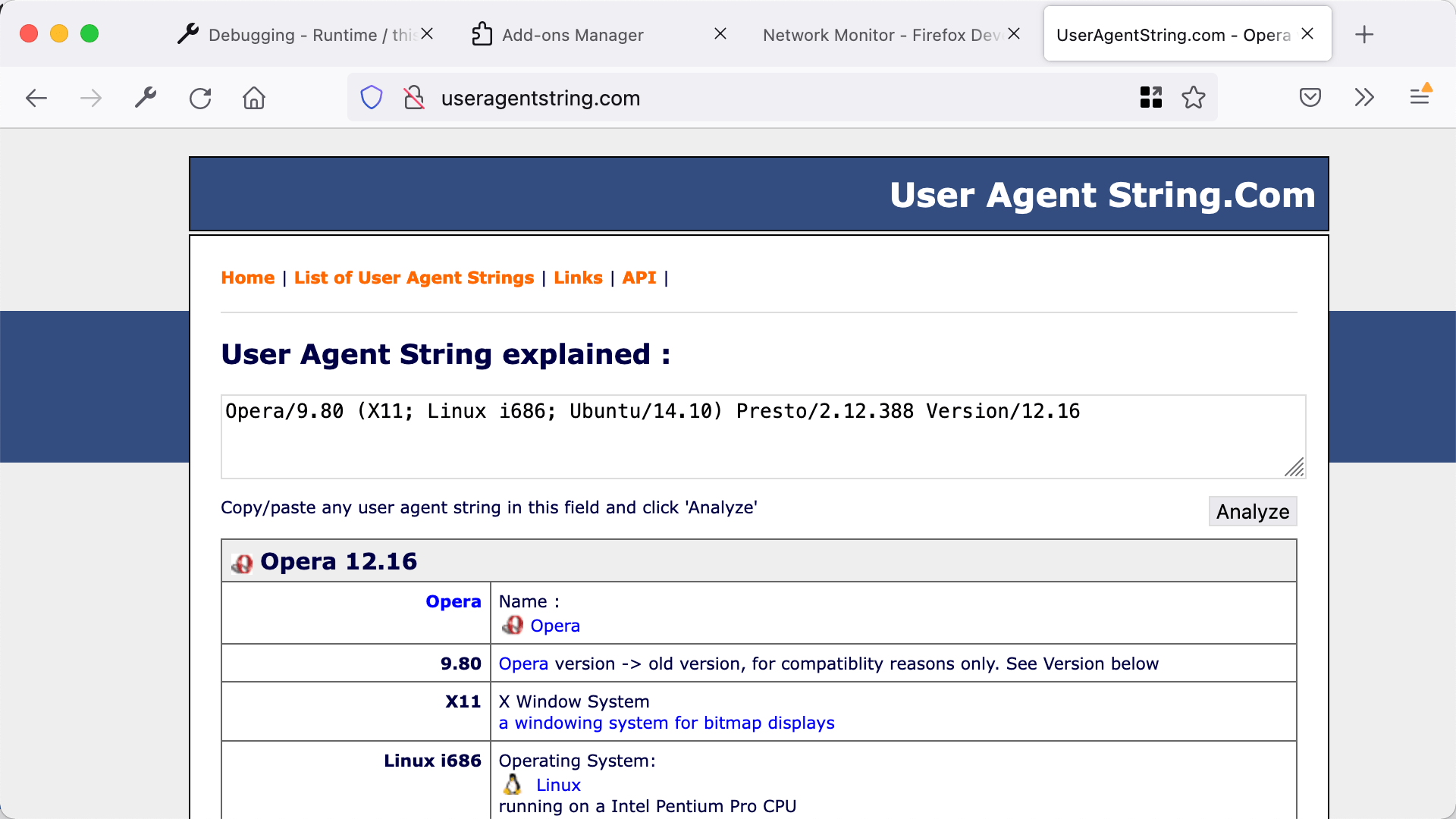
To test it out, open useragentstring.com and check that it identifies the browser as Firefox. Then reload the extension, reload useragentstring.com , and see that Firefox is now identified as Opera.
To learn about all the things you can do with the
webRequest
API, see its
参考文档编制
.
最后修改: , 由 MDN 贡献者