Searches for text in a tab.
You can use this function to search normal HTTP(S) web pages. It searches a single tab: you can specify the ID of a particular tab to search, or it will search the active tab by default. It searches all frames in the tab.
You can make the search case-sensitive and make it match whole words only.
By default, the function just returns the number of matches found. By passing in the
includeRangeData
and
includeRectData
options, you can get more information about the location of the matches in the target tab.
This function stores the results internally, so the next time any extension calls
find.highlightResults()
, then the results of this find call will be highlighted, until the next time someone calls
find()
.
This is an asynchronous function that returns a
Promise
.
browser.find.find(
queryphrase
,
// string
选项
// optional object
)
queryphrase
string
. The text to search for.
选项
可选
对象
. An object specifying additional options. It may take any of the following properties, all optional:
tabId
integer
. ID of the tab to search. Defaults to the active tab.
caseSensitive
boolean
. If true, the search is case-sensitive. Defaults to
false
.
entireWord
boolean
. Match only entire words: so "Tok" will not be matched inside "Tokyo". Defaults to
false
.
includeRangeData
boolean
. Include range data in the response, which describe where in the page DOM the match was found. Defaults to
false
.
includeRectData
boolean
. Include rectangle data in the response, which describes where in the rendered page the match was found. Defaults to
false
.
A
Promise
that will be fulfilled with an object containing up to three properties:
count
integer
. The number of results found.
rangeData
可选
array
。若
includeRangeData
给定在
选项
parameter, then this property will be included. It is provided as an array of
RangeData
objects, one for each match. Each
RangeData
object describes where in the DOM tree the match was found. This would enable, for example, an extension to get the text surrounding each match, so as to display context for the matches.
The items correspond to the items given in
rectData
,所以
rangeData[i]
describes the same match as
rectData[i]
.
每个
RangeData
contains the following properties:
framePos
The index of the frame containing the match. 0 corresponds to the parent window. Note that the order of objects in the
rangeData
array will sequentially line up with the order of frame indexes: for example,
framePos
for the first sequence of
rangeData
objects will be 0,
framePos
for the next sequence will be 1, and so on.
startTextNodePos
The ordinal position of the text node in which the match started.
endTextNodePos
The ordinal position of the text node in which the match ended.
startOffset
The ordinal position of the start of the match within its text node.
endOffset
The ordinal position of the end of the match within its text node.
rectData
可选
array
。若
includeRectData
给定在
选项
parameter, then this property will be included. It is an array of
RectData
objects. It contains client rectangles for all the text matched in the search, relative to the top-left of the viewport. Extensions can use this to provide custom highlighting of the results.
每个
RectData
object contains rectangle data for a single match. It has two properties:
rectsAndTexts
An object containing two properties, both arrays:
rectList
: an array of objects which each have four integer properties:
top
,
left
,
bottom
,
right
. These describe a rectangle relative to the top-left of the viewport.
textList
: an array of strings, corresponding to the
rectList
array. The entry at
textList[i]
contains the part of the match bounded by the rectangle at
rectList[i]
.
For example, consider part of a web page that looks like this:
 If you search for "You may", the match needs to be described by two rectangles:
If you search for "You may", the match needs to be described by two rectangles:
 In this case, in the
In this case, in the
RectData
that describes this match,
rectsAndTexts.rectList
and
rectsAndTexts.textList
will each have 2 items.
textList[0]
will contain "You ", and
rectList[0]
will contain its bounding rectangle.
textList[1]
will contain "may", and
rectList[1]
will contain
its
bounding rectangle.
text
The complete text of the match, "You may" in the example above.
BCD tables only load in the browser
Search the active tab for "banana", log the number of matches, and highlight them:
function found(results) {
console.log(`There were: ${results.count} matches.`);
if (results.count > 0) {
browser.find.highlightResults();
}
}
browser.find.find("banana").then(found);
Search for "banana" across all tabs (note that this requires the "tabs"
permission
or matching
host permissions
, because it accesses
tab.url
):
async function findInAllTabs(allTabs) {
for (let tab of allTabs) {
let results = await browser.find.find("banana", {tabId: tab.id});
console.log(`In page "${tab.url}": ${results.count} matches.`)
}
}
browser.tabs.query({}).then(findInAllTabs);
In this example the extension uses
rangeData
to get the context in which the match was found. The context is the complete
textContent
of the node in which the match was found. If the match spanned nodes, the context is the concatenation of the
textContent
of all spanned nodes.
Note that for simplicity, this example doesn't handle pages that contain frames. To support this you'd need to split
rangeData
into groups, one per frame, and execute the script in each frame.
The background script:
// background.js
async function getContexts(matches) {
// get the active tab ID
let activeTabArray = await browser.tabs.query({
active: true, currentWindow: true
});
let tabId = activeTabArray[0].id;
// execute the content script in the active tab
await browser.tabs.executeScript(tabId, {file: "get-context.js"});
// ask the content script to get the contexts for us
let contexts = await browser.tabs.sendMessage(tabId, {
ranges: matches.rangeData
});
for (let context of contexts) {
console.log(context);
}
}
browser.browserAction.onClicked.addListener((tab) => {
browser.find.find("example", {includeRangeData: true}).then(getContexts);
});
The content script:
/**
* Get all the text nodes into a single array
*/
function getNodes() {
let walker = document.createTreeWalker(document, window.NodeFilter.SHOW_TEXT, null, false);
let nodes = [];
while(node = walker.nextNode()) {
nodes.push(node);
}
return nodes;
}
/**
* Gets all text nodes in the document, then for each match, return the
* complete text content of nodes that contained the match.
* If a match spanned more than one node, concatenate the textContent
* of each node.
*/
function getContexts(ranges) {
let contexts = [];
let nodes = getNodes();
for (let range of ranges) {
let context = nodes[range.startTextNodePos].textContent;
let pos = range.startTextNodePos;
while (pos < range.endTextNodePos) {
pos++;
context += nodes[pos].textContent;
}
contexts.push(context);
}
return contexts;
}
browser.runtime.onMessage.addListener((message, sender, sendResponse) => {
sendResponse(getContexts(message.ranges));
});
In this example the extension uses
rectData
to "redact" the matches, by adding black DIVs over the top of their bounding rectangles:
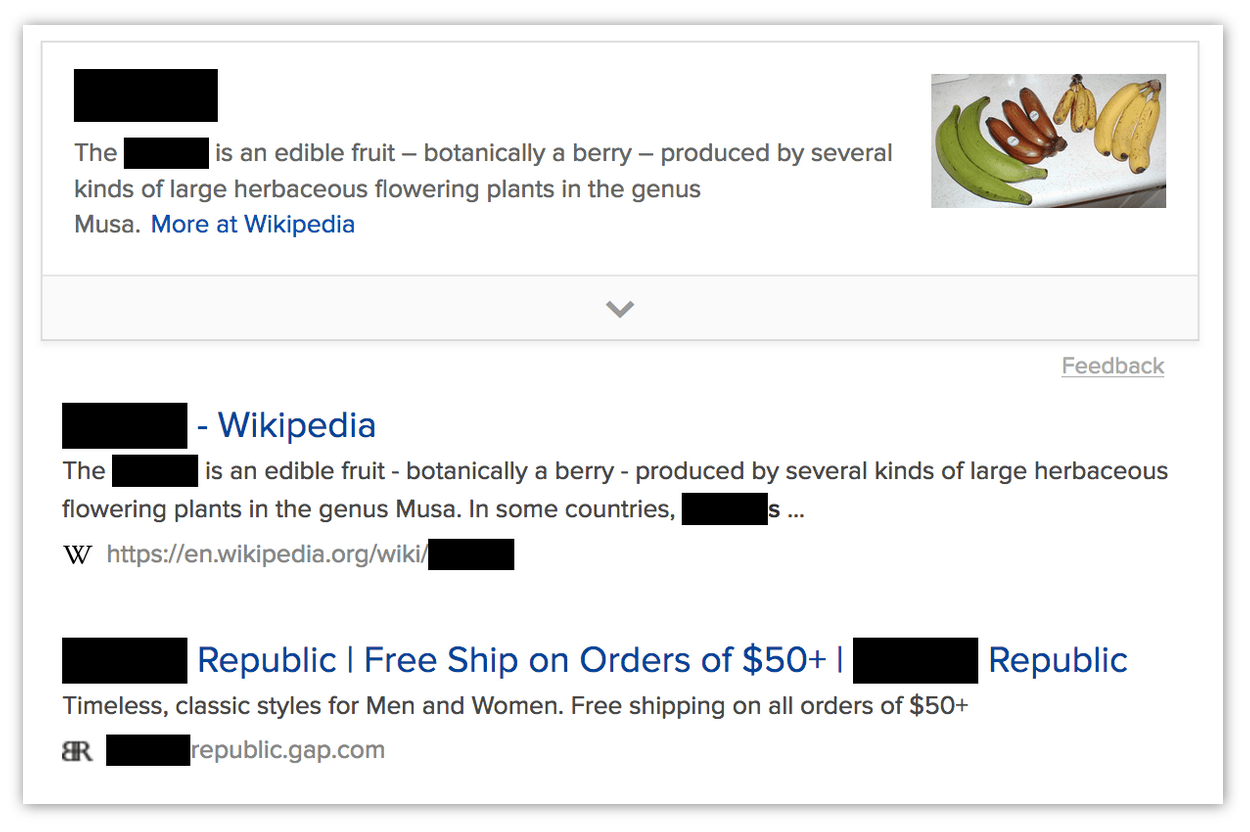 Note that in many ways this is a poor way to redact pages.
Note that in many ways this is a poor way to redact pages.
The background script:
// background.js
async function redact(matches) {
// get the active tab ID
let activeTabArray = await browser.tabs.query({
active: true, currentWindow: true
});
let tabId = activeTabArray[0].id;
// execute the content script in the active tab
await browser.tabs.executeScript(tabId, {file: "redact.js"});
// ask the content script to redact matches for us
await browser.tabs.sendMessage(tabId, {rects: matches.rectData});
}
browser.browserAction.onClicked.addListener((tab) => {
browser.find.find("banana", {includeRectData: true}).then(redact);
});
The content script:
// redact.js
/**
* Add a black DIV where the rect is.
*/
function redactRect(rect) {
var redaction = document.createElement("div");
redaction.style.backgroundColor = "black";
redaction.style.position = "absolute";
redaction.style.top = `${rect.top}px`;
redaction.style.left = `${rect.left}px`;
redaction.style.width = `${rect.right-rect.left}px`;
redaction.style.height = `${rect.bottom-rect.top}px`;
document.body.appendChild(redaction);
}
/**
* Go through every rect, redacting them.
*/
function redactAll(rectData) {
for (match of rectData) {
for (rect of match.rectsAndTexts.rectList) {
redactRect(rect);
}
}
}
browser.runtime.onMessage.addListener((message) => {
redactAll(message.rects);
});
最后修改: , 由 MDN 贡献者